Your ear is a very complex mechanism that turns vibrations into electrical signals, which your brain interprets as sound.
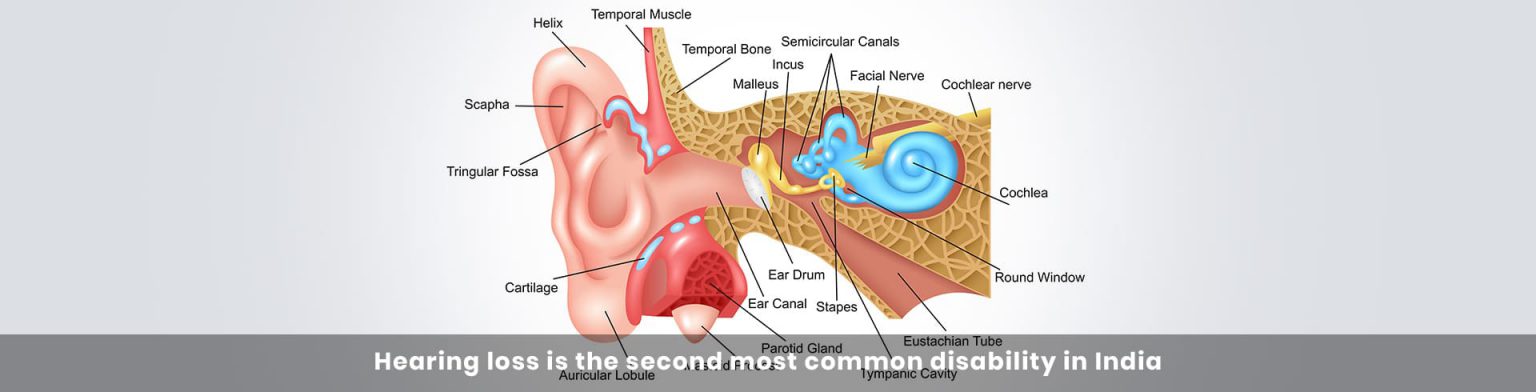

The process begins when sound waves travel through the air and into your ear canal. Your ear canal, in turn, funnels the sound waves down to your eardrum, which vibrates like the cone of a stereo speaker when the sound waves wash over it.
Then, three small bones, the hammer, anvil, and stirrup, transfer the vibrations to your inner ear and into your cochlea, which is shaped like a snail’s shell. The liquid inside your cochlea’s spiralling tubes vibrates and causes groups of microscopic hairs to wave back and forth.
Each group of hairs detects different wavelengths, or pitches, of sound, which allows you to differentiate between the high pitches of guitar notes and the rumbling sound of a bass guitar. And when the hairs bend to one pitch or another, they create a chemical reaction that sends electrical signals down the auditory nerve and into your brain.
And this opens up your vibrant world of music, conversation, and laughter.
We hear over different frequency ranges i.e. from 20 hertz to 20000 hertz and the normal limits of hearing are expressed in terms of decibels which should be 0 dB to 25 dB HL (hearing level) as per standards. If someone is not able to hear sounds at different frequency levels up to the level of 25 decibels, then the individual is said to have hearing loss.
As the normal speech conversation level range is 40-60 decibels, an individual with a mild loss ignores his hearing problem because he/she can manage by requesting people to speak aloud. Furthering the damage, the prevalent social stigma about hearing problems & hearing aids prevent the individual from getting his problem treated or even checked.
At Soft Hear Clinic, we emphasize regular complete examination and present summary prognosis to individuals who are keen to keep their hearing health intact. It is advised even for a normal individual to enroll for hearing threshold tests every 8-10 months as there are several damaging factors in the environment that can impair our hearing levels anytime. More so, with regular free checkups camps at Soft Hear Clinic, we thrive to provide meaningful education to the masses on their hearing health.
Hearing helps us to communicate and communication makes us the humans we are, therefore it is very important that we keep our hearing health upright and monitored.


As per a recent census report, about 6% of the population in our country suffers from a hearing loss, the number is staggeringly high and there is a need to conduct a thorough hearing evaluation for all. Unlike eyesight, the hearing problem is often detected much later and even when detected, people tend to ignore it till it becomes severe.
Types of hearing Loss
Conductive Hearing Loss
This is a condition where an obstruction hampers sound waves from reaching the inner ear. The most common causes are ear infections, excessive ear wax, fluid build-up behind the eardrum, perforation of the eardrum, and otosclerosis, which is a stiffening of the bones in the middle ear. Conductive hearing issues can be medically managed and even cured, and it can cause hearing loss from mild to a moderately severe degree.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
This is a condition where damaged hair cells in the cochlea hamper or even stop sound waves from being converted into the electrical signals that the auditory nerve sends to the brain. Aging is, by far, the most common cause, but exposure to loud noise, certain medications, and genetics are also known causes. Sensorineural hearing loss cannot yet be medically managed or cured, and it often ranges from mild to profound.
Mixed Hearing Loss
This is a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. While the conductive aspect may be medically managed or cured, the sensorineural aspect cannot. And, of course, mixed hearing loss can range from mild to profound.
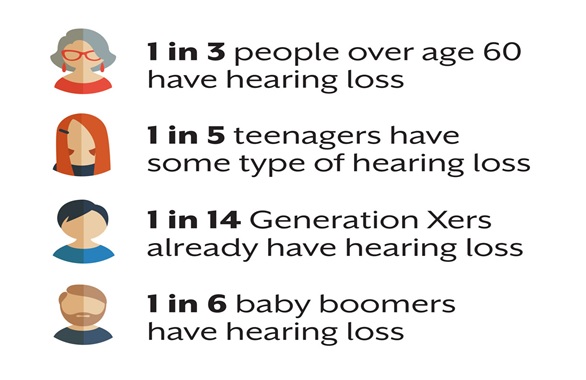
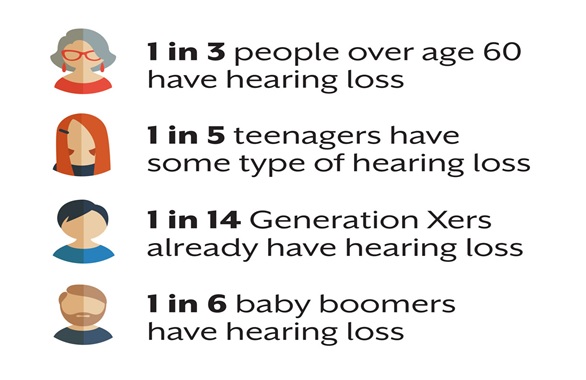
Hearing loss can occur at any time; however it is more prominent with increasing age. Hearing loss may affect the understanding of speech due to changes in the ability to hear certain frequencies as well as the clarity of speech, as this may often sound muffled or unclear.
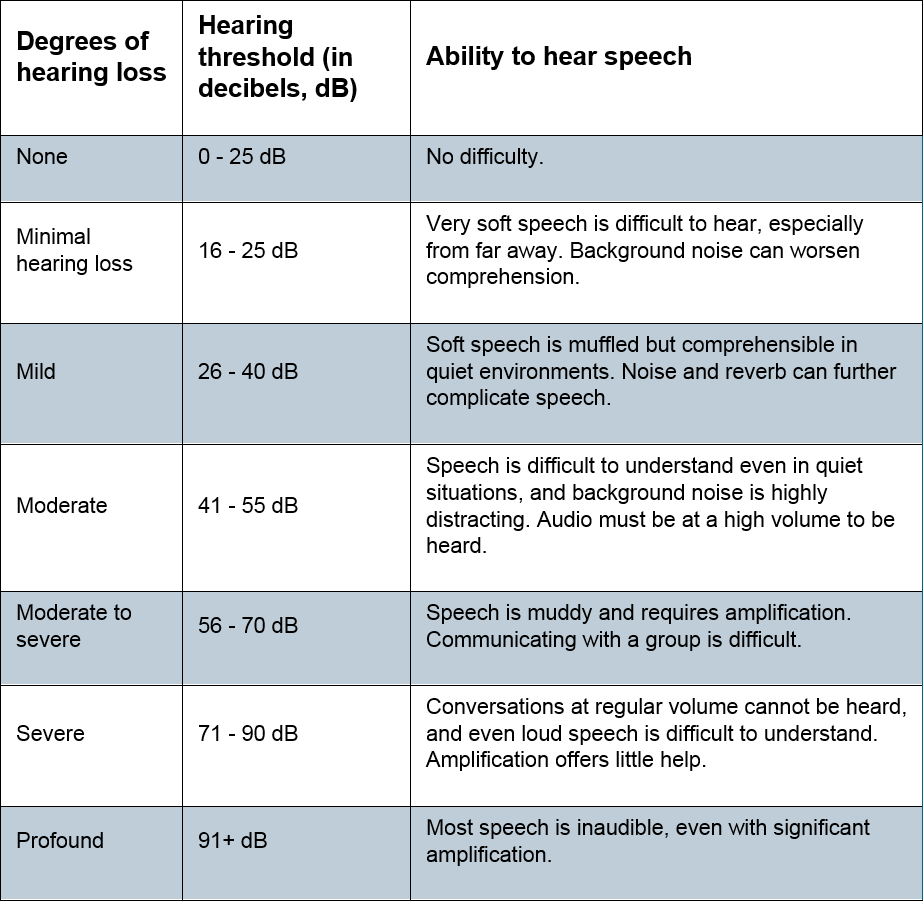
The degree of hearing loss can be classified as below:
Or

The Ability to Hear Well is Vital!
While mild hearing loss, such as the inability to hear a watch ticking, a bird singing, or the sound of quiet speech, may hardly seem drastic, it is equal to almost seven years of cognitive aging. Mild hearing loss can also increase a person’s likelihood of being stricken with dementia twofold as he or she grows older.
The likelihood of dementia increases with the severity of the hearing loss. For a person with moderate hearing loss, it increases threefold, and for someone with severe hearing loss, who can’t hear most speech, the potential for dementia increases five times over that of someone with normal hearing.
Hearing loss also causes strained relationships with friends and family. The mounting frustration over the inability to simply do what was so natural, before, such as carry on a conversation, can lead to depression, anxiety, and even worse.
Hearing loss has long been viewed as nothing more than an inconvenience. It’s anything but that. Hearing loss is a serious medical condition that can cause people to withdraw from their lives.
It doesn’t have to be a terrible affliction, though. The solution could be as easy as removing excessive ear wax or as complicated as having surgery done or getting hearing aids. But, whatever the solution is, it’s worth the effort, because yours or your loved one’s ability to hear is worth the effort.
What to look out for?
Hearing is one of our most important senses, yet many people who are facing its decline deny the inevitable truth. The signs of hearing problems are usually vague and develop gradually. On average it takes us over 7 years to actually get around to doing something about hearing problems. In that time, we tend to become used to “putting up with it”.
Are you experiencing symptoms?
Common Signs of Hearing Loss
- Asking others to repeat themselves
- Turning up the TV or radio to volume levels others find loud
- Having trouble understanding conversation in noisy places
- Feeling like other people mumble or slur their words
- Having trouble hearing women’s and/or children’s voices
- Having trouble hearing on the telephone
- Avoiding social situations that were once enjoyable
- Having trouble following a fast moving conversation
- Missing important information in meetings
- Being told by others that you have hearing loss.
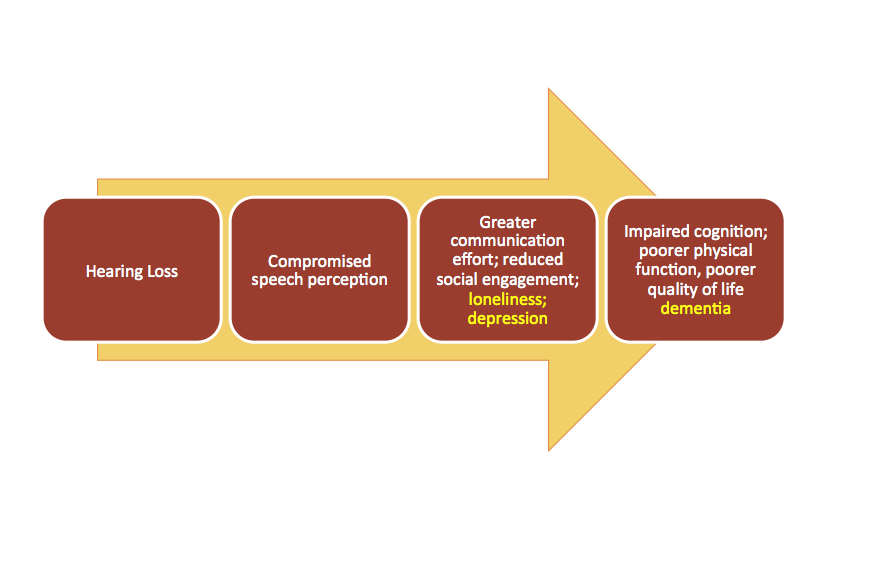

Over time, reduced stimulation to your ears and brain can actually impair the brain’s ability to process sound and recognize speech. The more speech recognition deteriorates, the more difficult it is to recover. When you can’t hear what’s going on around you, your mental sharpness suffers.
The sooner you take action, the sooner you put a stop to the negative effects of hearing loss, and the sooner you begin to regain sharpness, confidence and control.
Why put up with hearing loss when you don’t have to? Nine out of 10 people surveyed by the non-profit Better Hearing Institute indicated the quality of their life having improved with hearing aids.
The solution is simple
Communication is critical in life. Your job and social interactions are all the more rewarding when you can communicate confidently — and hearing is vital for that.
- Fewer instances of confusion and disorientation
- Increased ability to concentrate and multitask
- Better memory skills and a greater ability to learn new tasks
- Alertness and awareness of their personal safety
- Increased earning power and more control over their lives